Introduction
Patient-centered care is an essential component of high-quality healthcare, emphasizing the significance of considering patients' unique needs, preferences, and values when delivering medical services. This approach prioritizes providing personalized, compassionate, and coordinated care tailored to each individual patient's specific situation. By centering the patient in the healthcare experience, healthcare providers can enhance outcomes, increase patient satisfaction, and improve overall healthcare quality. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of patient-centered care. We will begin by exploring patient engagement and how it plays a crucial role in ensuring that patients feel heard and involved in their own healthcare journey. We will then discuss personalized treatment plans and how they help healthcare professionals tailor care to meet the unique requirements of each patient. Finally, we will focus on effective communication as a central component of patient-centered care, examining techniques and strategies to ensure clear and meaningful interaction between patients and healthcare providers.
Patient Engagement
Active Involvement in Care
Patient engagement is a fundamental aspect of patient-centered healthcare, where patients are actively involved in their own healthcare journey. Instead of being passive recipients of treatment, patients become active participants in understanding their condition, exploring treatment options, and making decisions based on informed knowledge. To achieve this, healthcare providers must adopt a collaborative approach that fosters a supportive and comfortable environment where patients can freely express their concerns and preferences. This approach requires providers to provide clear and concise information about patients' health conditions and treatment options in a manner that is tailored to their level of understanding. One effective way to enhance patient engagement is by providing education. By providing patients with accurate and relevant information, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment. This includes using visual aids and simplified language to help patients understand complex medical concepts.
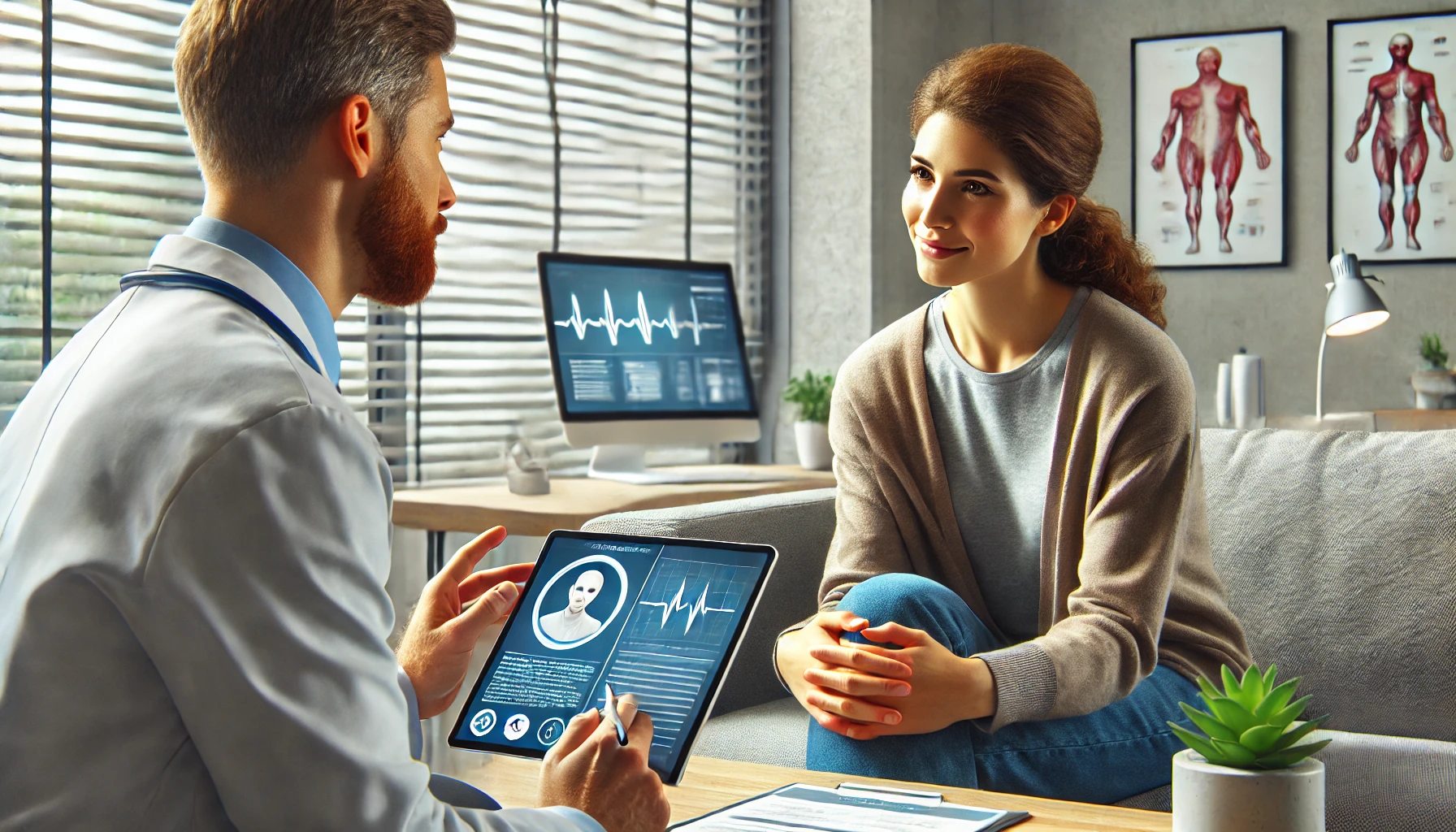

Shared Decision-Making
Shared decision-making is a vital component of patient engagement. It involves healthcare providers and patients working together to make decisions about the patient's care. This process acknowledges the patient's right to be fully informed and to participate in decisions that affect their health. Shared decision-making not only respects patient autonomy but also leads to better health outcomes, as patients who are involved in their care are more likely to adhere to treatment plans.
In practice, shared decision-making requires open communication and mutual respect. Healthcare providers should present all relevant information about the available treatment options, including the potential benefits, risks, and uncertainties. They should also listen to the patient's concerns, values, and preferences, and incorporate these into the decision-making process. Tools such as decision aids and structured consultations can facilitate this collaborative approach.
Empowering Patients
Empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare is another essential aspect of patient-centered care. Empowered patients are more likely to engage in self-care behaviors, manage chronic conditions effectively, and make lifestyle changes that promote better health. Empowerment involves providing patients with the knowledge, skills, and confidence they need to manage their health.
One effective strategy for empowering patients is to set achievable health goals and provide ongoing support to help them reach these goals. For example, a patient with diabetes might set a goal to maintain their blood sugar levels within a specific range. Healthcare providers can support this goal by offering regular monitoring, educational resources, and encouragement. Additionally, providing patients with access to their health records and involving them in tracking their progress can enhance their sense of ownership and control over their health.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Tailoring Care to Individual Needs
Personalized treatment plans are at the heart of patient-centered care. Every patient is unique, with different medical histories, cultural backgrounds, lifestyles, and preferences. Tailoring treatment plans to these individual factors ensures that care is more effective and relevant to each patient.
To create personalized treatment plans, healthcare providers must conduct comprehensive assessments that consider all aspects of the patient's life. This includes not only their medical history and current health status but also their social, emotional, and cultural context. Understanding these factors allows providers to develop treatment plans that are realistic, achievable, and aligned with the patient's values and goals.
For example, a patient with a chronic condition like hypertension might have a treatment plan that includes medication, dietary changes, and regular exercise. However, the specifics of this plan should be tailored to the patient's cultural dietary preferences, physical capabilities, and personal motivations. By considering these individual factors, healthcare providers can create a more personalized and effective plan.
Cultural Competence
Cultural competence is a critical aspect of developing personalized treatment plans. It involves understanding and respecting the cultural differences that influence a patient's health beliefs and behaviors. Culturally competent care ensures that treatment plans are not only medically sound but also culturally appropriate and respectful.
Healthcare providers can enhance their cultural competence by seeking to understand the cultural backgrounds of their patients, engaging in ongoing education about cultural diversity, and developing communication skills that bridge cultural gaps. For instance, a provider treating a patient from a community with specific dietary restrictions should be aware of these restrictions and incorporate them into the treatment plan.
Incorporating Patient Preferences
Incorporating patient preferences into treatment plans is essential for patient-centered care. Patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans that reflect their values, preferences, and lifestyles. This involves asking patients about their preferences and making accommodations whenever possible.
For example, some patients may prefer non-pharmacological treatments for managing pain, such as physical therapy or acupuncture. Others may have specific preferences regarding the timing and frequency of medical appointments. By respecting these preferences and incorporating them into the treatment plan, healthcare providers can enhance patient satisfaction and adherence.
Effective Communication
Building Trust and Rapport
Effective communication is fundamental to patient-centered care. It is the foundation upon which trust and rapport between patients and healthcare providers are built. Trusting relationships are crucial for ensuring that patients feel comfortable sharing their concerns, asking questions, and participating in their care.
Building trust requires healthcare providers to be approachable, empathetic, and respectful. Active listening is a critical communication skill that involves fully concentrating on the patient, understanding their message, and responding thoughtfully. By demonstrating genuine interest and concern for the patient's well-being, providers can foster a trusting and supportive relationship.
Clear and Transparent Communication
Clear and transparent communication is essential for ensuring that patients understand their health conditions, treatment options, and the potential outcomes. Healthcare providers must communicate information in a way that is easy to understand, avoiding medical jargon and using plain language instead.
Using visual aids, diagrams, and written materials can enhance understanding, especially for complex medical information. Additionally, verifying patient comprehension through techniques such as teach-back, where patients repeat the information in their own words, can ensure that they have understood the key points.
Addressing Concerns and Questions
Addressing patients' concerns and questions is a critical aspect of effective communication. Patients often have fears, anxieties, and uncertainties about their health and treatment. Healthcare providers should create an open and non-judgmental environment where patients feel comfortable expressing these concerns.
Taking the time to listen to patients' questions and providing thorough, thoughtful answers can alleviate anxiety and build confidence in the treatment plan. This dialogue helps to ensure that patients feel heard and respected, which is vital for maintaining their trust and engagement.
Coordination of Care
Integrated and Aligned Health Services
Coordination of care is a fundamental aspect of patient-centered care, ensuring that all healthcare services are integrated and aligned with the patient's goals and needs. Effective coordination minimizes fragmentation of care, reduces the risk of errors, and enhances the overall patient experience. This requires seamless communication and collaboration among all members of the healthcare team, including primary care providers, specialists, nurses, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals.
One approach to improving care coordination is the implementation of care teams, where a group of healthcare providers works together to manage a patient's care. Each team member brings their expertise to the table, ensuring that the patient receives comprehensive and holistic care. For example, a patient with diabetes might have a care team that includes an endocrinologist, a nutritionist, a diabetes educator, and a primary care physician. This team collaborates to create and implement a cohesive care plan that addresses all aspects of the patient's health.
Transition of Care
Effective care coordination is especially critical during transitions of care, such as when a patient is discharged from the hospital or transferred between different care settings. These transitions can be vulnerable points in the patient care continuum, where miscommunication or lack of follow-up can lead to adverse outcomes.
To ensure smooth transitions, healthcare providers should implement standardized processes for handoffs and communication. This includes providing detailed discharge summaries, medication reconciliation, and clear follow-up instructions. Additionally, involving patients and their families in the transition process can help ensure that they understand the next steps in their care journey and know who to contact if they have questions or concerns.
Use of Health Information Technology
Health information technology (HIT) plays a vital role in enhancing care coordination. Electronic health records (EHRs) and other digital tools enable the seamless sharing of patient information across different healthcare settings, ensuring that all providers have access to up-to-date and comprehensive patient data.
EHRs can facilitate better communication among providers by allowing them to view and update patient records in real time. Additionally, patient portals can give patients access to their health information, enabling them to track their progress, view test results, and communicate with their healthcare team. By leveraging HIT, healthcare providers can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of care coordination, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.

Empowerment
Encouraging Self-Care and Self-Management
Empowerment is a core principle of patient-centered care, encouraging patients to take an active role in their healthcare and promoting self-care and self-management of chronic conditions. Empowered patients are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors, adhere to treatment plans, and make informed decisions about their health.
One effective strategy for empowering patients is providing them with the tools and resources they need to manage their health. This can include educational materials, support groups, and digital health tools such as mobile apps and wearable devices. For example, a patient with hypertension might use a mobile app to track their blood pressure, set medication reminders, and receive personalized tips for managing their condition.
Building Health Literacy
Health literacy is a critical component of patient empowerment. Patients with higher health literacy are better equipped to understand health information, navigate the healthcare system, and make informed decisions about their care. Healthcare providers can enhance health literacy by providing clear and accessible information and using plain language to explain medical terms and concepts.
Interactive and engaging educational materials, such as videos, infographics, and decision aids, can also help improve health literacy. Additionally, healthcare providers should assess patients' understanding of the information provided and use teach-back methods to confirm comprehension. By building health literacy, providers can empower patients to take control of their health and make informed choices.
Supporting Behavioral Change
Behavioral change is often necessary for managing chronic conditions and improving overall health. Healthcare providers can support patients in making positive behavioral changes by using motivational interviewing techniques, setting realistic and achievable goals, and providing ongoing encouragement and support.
Motivational interviewing is a patient-centered counseling approach that helps patients explore and resolve ambivalence about behavior change. This technique involves open-ended questions, reflective listening, and affirmations to help patients identify their motivations for change and develop a plan to achieve their goals.
For example, a patient with obesity who wants to lose weight might work with their healthcare provider to set small, achievable goals such as increasing physical activity or making healthier dietary choices. Regular follow-up appointments and check-ins can provide the support and accountability needed to sustain these changes over time.
Respect for Patient Autonomy
Informed Decision-Making
Respecting patient autonomy is a fundamental aspect of patient-centered care. It involves recognizing and honoring patients' rights to make informed decisions about their health and treatment. Healthcare providers can support patient autonomy by ensuring that patients have all the information they need to make informed choices and by respecting their preferences and decisions.
Informed decision-making requires clear and transparent communication about the benefits, risks, and alternatives of different treatment options. Healthcare providers should take the time to discuss these options with patients, answer their questions, and ensure that they fully understand their choices. Decision aids, such as pamphlets, websites, and interactive tools, can also help patients weigh the pros and cons of different options and make decisions that align with their values and goals.
Advanced Care Planning
Advanced care planning is another important aspect of respecting patient autonomy. It involves discussing and documenting patients' preferences for future healthcare, including end-of-life care. This ensures that patients' wishes are respected and honored, even if they are unable to communicate them at a later time.
Healthcare providers should initiate conversations about advanced care planning early and revisit these discussions periodically. This can include talking about advance directives, living wills, and appointing a healthcare proxy. By having these conversations, patients can make informed decisions about their future care, and healthcare providers can ensure that their treatment aligns with their wishes.
Cultural Sensitivity and Respect
Cultural sensitivity and respect are essential for honoring patient autonomy and providing patient-centered care. Healthcare providers should be aware of and sensitive to the cultural, religious, and personal values that influence patients' health beliefs and decisions. This involves taking the time to understand each patient's unique background and preferences and incorporating these into the care plan.
For example, some patients may have cultural or religious beliefs that influence their preferences for certain treatments or procedures. Healthcare providers should respect these beliefs and work with patients to find acceptable and effective alternatives. By demonstrating cultural sensitivity and respect, providers can build trust and rapport with patients, enhancing the overall quality of care.
Outcomes of Patient-Centered Care
Improved Health Outcomes
Patient-centered care has been shown to significantly improve health outcomes. By tailoring treatment plans to the individual needs and preferences of patients, healthcare providers can ensure that interventions are more effective and relevant. Patients who are actively engaged in their care and who feel that their voices are heard are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, manage their conditions effectively, and make healthier lifestyle choices.
For instance, studies have shown that patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension achieve better control over their conditions when they are involved in shared decision-making and personalized care planning. This leads to fewer complications, reduced hospital admissions, and overall better health outcomes. Additionally, the continuous monitoring and feedback provided by digital health tools and wearables can help in early detection of potential issues, allowing for prompt intervention and preventing the escalation of health problems.
Enhanced Patient Satisfaction
Patient satisfaction is a critical measure of healthcare quality, and patient-centered care is strongly associated with higher satisfaction levels. When patients feel respected, listened to, and involved in their care decisions, their experience of healthcare is significantly more positive. This not only enhances their satisfaction but also builds trust and loyalty towards their healthcare providers.
Effective communication, cultural sensitivity, and respect for patient autonomy contribute to a more satisfactory healthcare experience. Patients appreciate when healthcare providers take the time to explain conditions and treatments in a clear and understandable manner, address their concerns, and respect their cultural and personal values. The positive relationships fostered through patient-centered care lead to higher patient satisfaction, which in turn can improve adherence to treatment plans and overall health outcomes.
Reduced Healthcare Costs
Patient-centered care can also lead to reduced healthcare costs by improving the efficiency and effectiveness of care delivery. By focusing on preventive care, early intervention, and effective management of chronic conditions, patient-centered care reduces the need for costly emergency interventions and hospitalizations. Additionally, better coordination of care and the use of health information technology can minimize duplication of services and prevent medical errors, further reducing costs.
For example, a patient-centered approach to managing chronic diseases like heart disease or diabetes involves regular monitoring, patient education, and personalized care plans. This proactive management helps prevent complications that might otherwise require expensive treatments or hospital stays. Furthermore, empowered patients who actively engage in self-care are less likely to require intensive healthcare services, leading to overall cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems.
Strengthened Patient-Provider Relationships
The emphasis on communication, trust, and respect in patient-centered care leads to stronger relationships between patients and healthcare providers. These strong relationships are the foundation of effective healthcare, as they encourage open dialogue, mutual respect, and a collaborative approach to care. When patients feel that their providers truly care about their well-being and respect their input, they are more likely to be honest about their symptoms, follow medical advice, and engage in their treatment plans.
Strong patient-provider relationships also enhance continuity of care, as patients are more likely to return to providers they trust for ongoing care and follow-up. This continuity is essential for managing chronic conditions, monitoring health changes, and providing consistent care over time. The trust and rapport built through patient-centered care contribute to a more positive healthcare experience and better health outcomes.
Implementing Patient-Centered Care
Organizational Commitment
Implementing patient-centered care requires a commitment from healthcare organizations at all levels. This commitment involves creating a culture that prioritizes patient-centered values, investing in staff training and development, and implementing systems and processes that support patient-centered practices. Leadership must champion these values and ensure that they are integrated into the organization’s mission, policies, and daily operations.
For example, healthcare organizations can develop training programs that focus on communication skills, cultural competence, and shared decision-making. By equipping healthcare providers with the necessary skills and knowledge, organizations can ensure that patient-centered care is consistently delivered across all interactions.
Patient and Family Involvement
Engaging patients and their families in the design and delivery of healthcare services is crucial for implementing patient-centered care. This involvement can take many forms, from including patients in care planning and decision-making to seeking their input on organizational policies and practices. Patient advisory councils, focus groups, and satisfaction surveys are effective ways to gather feedback and involve patients in the continuous improvement of care services.
For instance, involving patients in the development of educational materials or care protocols can ensure that these resources are relevant and accessible. Patient and family involvement helps healthcare organizations understand the patient perspective, identify areas for improvement, and develop solutions that meet the real needs of patients.
Use of Technology
Technology plays a significant role in supporting patient-centered care by enhancing communication, coordination, and patient engagement. Electronic health records (EHRs), patient portals, telehealth services, and mobile health applications are essential tools for implementing patient-centered practices.
EHRs facilitate the seamless sharing of patient information among providers, ensuring that care is coordinated and comprehensive. Patient portals allow patients to access their health information, communicate with their healthcare team, and manage appointments, enhancing transparency and engagement. Telehealth services provide convenient access to care, particularly for patients with mobility issues or those living in remote areas. Mobile health applications and wearable devices enable patients to monitor their health, set goals, and receive personalized feedback, empowering them to take an active role in their care.
Continuous Improvement
Patient-centered care is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation and improvement. Healthcare organizations should regularly assess their practices, gather feedback from patients and staff, and implement changes to enhance care delivery. Quality improvement initiatives, patient satisfaction surveys, and performance metrics are valuable tools for monitoring progress and identifying areas for enhancement.
For example, regular patient satisfaction surveys can provide insights into patients’ experiences and highlight areas where improvements are needed. Quality improvement teams can then use this feedback to develop and implement strategies for enhancing patient-centered practices. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, healthcare organizations can ensure that patient-centered care remains a priority and continues to evolve in response to patients’ needs.
Conclusion
Patient-centered care is essential for delivering high-quality health services that meet the needs, preferences, and values of patients. By focusing on patient engagement, personalized treatment plans, effective communication, care coordination, empowerment, and respect for patient autonomy, healthcare providers can create a compassionate, coordinated, and responsive healthcare experience.
Implementing patient-centered care requires organizational commitment, patient and family involvement, the use of technology, and continuous improvement. By embracing these principles, healthcare organizations can enhance health outcomes, improve patient satisfaction, reduce healthcare costs, and strengthen patient-provider relationships.
At MedCarePro, we are dedicated to providing high-quality, patient-centered care. We believe that by putting patients at the center of everything we do, we can deliver better health outcomes and a more positive healthcare experience. Stay tuned to our blog for more insights and information on how patient-centered care is transforming healthcare and how we are committed to making a difference in the lives of our patients.